JB-16 Slope Protection Materials
Slope Protection
The foundation of slope protection is generally arranged on favorable sub grade, and drain holes are made according to relevant requirements so as to prevent spalling and collapse of the slope due to rain scouring or weathering.
Slope Protection Basics
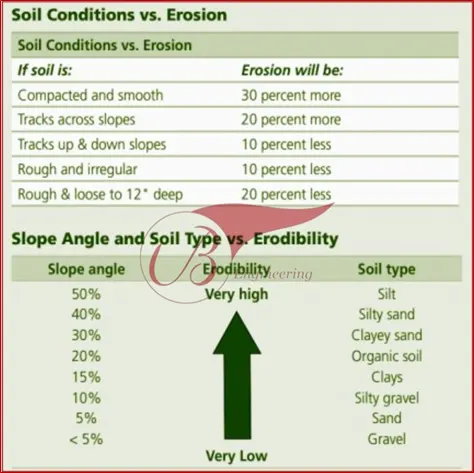
Protecting slopes from erosion requires several actions that must be taken together. No single approach will be successful, especially if the slope is steep or has highly erodible soils (see below).
JB Engineering uses one or more of the following actions to reduce erosion on slopes:
- Divert upland runoff
- Control slope runoff
- Till seedbed or condition the soil
- Seed and mulch
- Silt fence or brush barrier
- Retaining wall
- Blankets or armoring
Types of Slope Protection:-
1. JB Engineering Silt Fence
Defination: A silt fence is a temporary sediment barrier consisting of filter fabric entrenched into the soil and attached to supporting posts. Silt fences are downhill from bare soil areas and are installed with a trencher or by a slicing machine to prevent against common silt fence failures.

Purpose: Silt fences are common sediment control devices. Silt fencing should be installed where sediment-laden water can pond, thus allowing the sediment to fall out of suspension and separate from the runoff. Runoff will also bleed through the silt fence fabric, providing physical filtering for larger sediment particles. Reasons for the high failure rate of improperly designed (located) and installed silt fence include:
- Improper placement on the site
- Allowing excessive drainage area to the silt fence structure
- Shallow trenches with little or no soil compaction
- Inadequate attachment to posts
- Failure to maintain the silt fence after installation
- Installing silt fence along property boundaries, producing concentrated runoff.
2. JB Engineering Brush, Rock, and Other Sediment Barriers
Defination: Brush, rock, and other commercial barriers can be used as a temporary sediment barrier instead of a silt fence.
Purpose: The purpose of any sediment barrier is to provide a place where sediment-laden water can pond, thus allowing the sediment to fall out of suspension and separate from the runoff.

3. JB Engineering Erosion Control Blankets (ECBs) and Turf Reinforcement Mats (TRMs)-
Defination: Temporary erosion control blankets (ECBs) and permanent turf reinforcement mats (TRMs), known generally as rolled erosion control products are single or multiple layer sheets composed of natural or synthetic material that is woven, sewn, bonded, or otherwise manufactured for placement on bare soil slopes or flow channels. They have been described as a temporary, degradable products composed of processed natural or polymer fibers mechanically, structurally, or chemically bound together to form a continuous matrix to provide erosion control and facilitate vegetation establishment.
Purpose: The purpose of any sediment barrier is to provide a place where sediment-laden water can pond, thus allowing the sediment to fall out of suspension and separate from the runoff.


Purpose: Erosion control blankets (ECBs) are used to temporarily stabilize and protect disturbed soil from raindrop impact and surface erosion, to increase infiltration, decrease compaction and soil crusting, and to conserve soil moisture. Mulching with ECBs will increase the germination rates for grasses and legumes and promote vegetation establishment. ECBs also protect seeds from predators; reduce desiccation and evaporation by insulating the soil and seed environment.
Some types of ECBs and turf reinforcement mats are specifically designed to stabilize channelized flow areas. These blankets and mats can aid the establishment of vegetation in waterways and increase the maximum permissible velocity of the given channel by reinforcing the soil and vegetation to resist the forces of erosion during runoff events. Stems, roots and rhizomes of the vegetation become intertwined with the mat, reinforcing the vegetation and anchoring the mat.

4. JB Engineering Temporary Slope Drains
Definition: Erosion control blankets (ECBs) are used to temporarily stabilize and protect disturbed soil from raindrop impact and surface erosion, to increase infiltration, decrease compaction and soil crusting, and to conserve soil moisture. Mulching with ECBs will increase the germination rates for grasses and legumes and promote vegetation establishment. ECBs also protect seeds from predators; reduce desiccation and evaporation by insulating the soil and seed environment.
Purpose: Temporary slope drains serve to convey concentrated runoff down the face of a cut or fill slope without causing erosion. They are generally used in conjunction with diversions to convey runoff down a slope until permanent water management measures can be installed.
Inspection and Maintenance: Inspect slope drains and supporting diversions weekly and after every significant rainfall and promptly make necessary repairs. When the protected area has been permanently stabilized, temporary measures can be removed, materials disposed of properly, and all disturbed areas stabilized appropriately.

5. JB Engineering Gabion Baskets and Mattresses
Definition: Gabions are rectangular galvanized wire baskets filled with stones used as pervious, semiflexible building blocks for slope and channel stabilization. Live rooting branches can be placed between the rock-filled baskets.
Purpose: Gabions protect slopes and stream banks from the erosive forces of moving water. Rock filled gabion baskets or mattresses can be used as retaining walls for slopes, to armor the bed or banks of channels, or to divert flow away from eroding channel sections. Rock-filled or vegetated rock gabions are used on stream bank sections subject to excessive erosion because of increased flows or disturbance during construction.

Gabion walls are appropriate where:
- An excessively steep stream bank must be stabilized and vegetative or extreme mechanical means of stabilization (i.e., pulling back bank) are not feasible because of site conditions.
- The vertical integrity of a soil bank needs a higher tensile strength to reduce sloughing of the stream bank.
- There is moderate to excessive subsurface water movements that could be creating erosion and damaging other types of no permeable structures.
- The slope must be modified while heavy machinery is unavailable to the site.
- Fill must be disposed of along an eroding stream bank (fill can be placed behind gabion to modify slope).
- A retaining or toe wall is needed to stabilize the slope.

- Rock riprap is an appropriate practice, but the available or desired rock size (smaller) is not sufficient alone to resist the expected shear stress exerted on the revetment. Gabions allow the use of a smaller size rock than would be possible without the wire baskets because the rock is bound by the wire mesh, creating a more monolithic structure.
6. JB Engineering Cellular Confinement Systems
Definition: A cellular confinement system (CCS) is a three-dimensional, honeycombed, sheet, mat, or interlocking structure filled with soil and planted with vegetation used to stabilize the surface of earthen cut and fill slopes.
Purpose: CCSs are permanent erosion control practices intended to stabilize infill materials for slope and channel protection, load support, and earth retention applications. The expandable panel creates a cellular system that confines topsoil infill, protects and reinforces the plant’s root zone and permits infiltration and natural subsurface drainage. The honeycomb shaped cells encapsulate and prevent erosion of the infill material.

The cellular confinement systems are used for:
- Revetments- Filling the cells with topsoil or rock and vegetation can provide an alternative to hard armor revetment systems.
- Erosion control on steep slopes- FCells can be filled with soil and vegetated or filled with granular materials. Slopes as steep as 1H:1V can be treated with cellular confinement systems. Application on steep slopes may require tendons for system stability and security against sliding.
- Flexible channel lining systems- either vegetated or rock filled.
- Road stabilization- cells confine and reinforce select fill materials, thereby increasing load-bearing capacities. Creates a porous pavement system with aggregate or topsoil/vegetation infill.
- Temporary low water stream crossings.
